Blockchain technology has been making waves in the world of finance and technology since the emergence of Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, in 2009. However, for many people, the concept of blockchain can still be confusing and daunting. In this article, we will provide a beginner’s guide to blockchain, cryptocurrency, and decentralized networks, and how they work together.
What Is Blockchain ?
At its simplest, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Each block in the blockchain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Once a block is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, making it a secure and transparent record of all transactions.
One of the most important features of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. Instead of being controlled by a central authority, such as a bank, blockchain is managed by a network of users. This means that no single entity has control over the network, making it more secure and resistant to tampering or hacking.
How Blockchain Works ?
Blockchain is a decentralized, digital ledger that is used to record transactions across many computers in a way that is secure, transparent, and tamper-proof. The basic idea behind blockchain is to create a public database that is maintained by a network of computers, rather than a single entity, making it virtually impossible for anyone to alter the data without the consensus of the network.
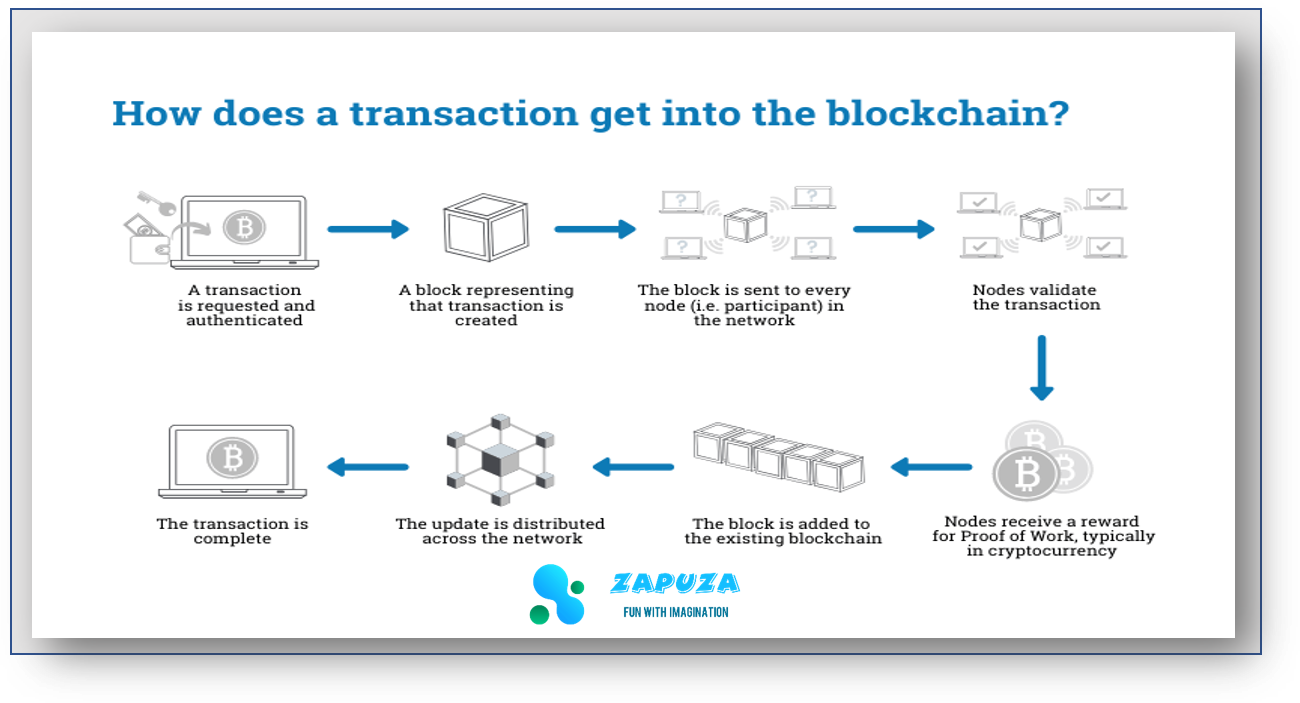
Here’s how it works:
A transaction is initiated: A transaction is created and broadcast to the network. This can be any type of transaction, such as a financial transfer, a purchase, or the exchange of information.
Verification: Nodes on the network (known as “miners”) verify the transaction using complex algorithms to ensure that it is valid. This involves verifying that the sender has sufficient funds, that the transaction is not a duplicate, and that the transaction meets the criteria for inclusion in a block.
Creation of a block: Once a transaction is verified, it is added to a block along with other verified transactions. This block is then broadcast to the network for validation.
Validation: Each node on the network independently verifies the block, checking to make sure that all of the transactions in the block are valid and that the block has not been tampered with. If the block is valid, it is added to the blockchain.
Addition to the blockchain: Once a block is added to the blockchain, it is considered to be a permanent part of the ledger. This means that it cannot be altered or deleted without the consensus of the network.
Distribution: Copies of the blockchain are distributed to all nodes on the network, ensuring that every participant has a complete and up-to-date record of all transactions.
What is Crypto-Currency ?
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security and operates independently of a central bank or financial institution. It is decentralized, meaning that it is not controlled by any single entity or government. Instead, it uses a distributed ledger technology, such as blockchain, to record transactions and manage the issuance of new units.
Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin, are created through a process called mining, which involves solving complex mathematical algorithms using computer processing power. Once a block of transactions is verified and added to the blockchain, a reward is given to the miner who solved the algorithm.
Cryptocurrency can be bought and sold on cryptocurrency exchanges, and it can be used as a means of payment for goods and services where it is accepted. Cryptocurrencies can also be stored in digital wallets, which can be accessed using private keys to authorize transactions.
One of the main advantages of cryptocurrency is that it offers a high degree of security and privacy, as transactions are recorded on a public ledger but are anonymous and cannot be altered once confirmed. However, cryptocurrencies can also be volatile and subject to market fluctuations, which can make them a risky investment.
What is decentralized network ?
A decentralized network is a type of network in which there is no central authority or single point of control. Instead, the network is composed of multiple nodes or participants that are connected to each other, allowing for the sharing of resources, data, and processing power.

In a decentralized network, each node is responsible for maintaining a copy of the network’s data or ledger, and any changes to the data or network must be validated by consensus among the nodes. This allows for a high degree of security and resilience, as the network can continue to operate even if some nodes fail or are compromised.
Decentralized networks can be used for a wide range of applications, such as peer-to-peer file sharing, social networks, online marketplaces, and even cryptocurrencies. They offer many advantages over centralized systems, such as increased privacy, transparency, and resilience, as well as reduced risk of censorship or single-point-of-failure attacks.
Overall, decentralized networks represent a paradigm shift in the way that we think about digital infrastructure, as they allow for more open, democratic, and secure systems that can better serve the needs of users and communities.