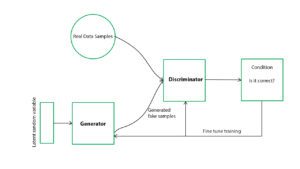
Abstract
Blockchain is an emerging technology that offers a range of opportunities for promoting sustainable agriculture. It provides a decentralized, tamper-proof database that can enable secure and transparent transactions across the food supply chain. This paper examines the potential of blockchain for enhancing sustainability in agriculture, including its role in improving traceability, increasing efficiency, and reducing waste. The challenges and opportunities of blockchain in sustainable agriculture are also discussed, including technical, regulatory, and social issues. The paper concludes with recommendations for future research and practical implementation of blockchain in sustainable agriculture.
Introduction
I. Introduction
A. Overview
Sustainable agriculture is an important issue that requires innovative solutions to address challenges such as resource depletion, environmental degradation, and food insecurity. Blockchain technology has the potential to offer such solutions by enhancing transparency, efficiency, and trust in the food supply chain. Blockchain provides a decentralized, tamper-proof database that can record and verify transactions between parties without the need for intermediaries such as banks or governments. This paper examines the role of blockchain in promoting sustainable agriculture, including its benefits, challenges, and opportunities.



B. Blockchain In Agriculture
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the agriculture industry by enhancing transparency, efficiency, and security in the food supply chain. Here are some ways in which blockchain can be used in agriculture:
- Traceability: With blockchain, every transaction along the supply chain can be recorded and verified, enabling farmers, suppliers, processors, retailers, and consumers to trace the origin, production, and distribution of food products from farm to fork. This can help prevent food fraud, reduce waste, and ensure the safety and quality of food products.
- Supply chain management: Blockchain can reduce the time and costs associated with administrative tasks, such as record-keeping, inventory management, and payment processing. It can also enable automated smart contracts that can facilitate real-time transactions between parties. This can help optimize resource allocation, reduce waste, and improve profitability for all stakeholders.
- Certification: Blockchain can be used to certify organic, fair trade, and other sustainable farming practices. By providing a tamper-proof record of transactions, blockchain can help ensure that farmers are paid fairly for their produce and that they follow sustainable farming practices. This can help reduce the environmental impact of agriculture, promote social responsibility, and enhance the resilience of the food system.
- Climate-smart agriculture: Blockchain can be used to promote climate-smart agriculture by enabling the monitoring and verification of carbon sequestration, water management, and other sustainable practices. By providing a transparent and secure platform for the exchange of data, blockchain can enable farmers to access incentives for sustainable practices and contribute to climate mitigation efforts.
- Agricultural finance: Blockchain can be used to facilitate agricultural finance by enabling the verification of creditworthiness, collateral, and repayment history. By providing a transparent and secure platform for transactions, blockchain can enable farmers to access financing at lower costs and with reduced risk.
Benefits of Blockchain in Sustainable Agriculture
Blockchain can enhance sustainability in agriculture in several ways. One of the most significant benefits is improved traceability, which can help prevent food fraud, reduce waste, and ensure the safety and quality of food products. With blockchain, every transaction along the supply chain can be recorded and verified, enabling consumers and regulators to trace the origin, production, and distribution of food products from farm to fork. This can also help identify and address issues related to environmental sustainability and social responsibility, such as deforestation, labor exploitation, and animal welfare.
Another benefit of blockchain in sustainable agriculture is increased efficiency. Blockchain can reduce the time and costs associated with administrative tasks, such as record-keeping, inventory management, and payment processing. It can also enable automated smart contracts that can facilitate real-time transactions between farmers, suppliers, processors, and retailers. This can help optimize resource allocation, reduce waste, and improve profitability for all stakeholders.
Challenges and Opportunities of Blockchain in Sustainable Agriculture
Despite its potential benefits, blockchain faces several challenges in sustainable agriculture. One of the main challenges is technical complexity, as blockchain requires significant computational resources and specialized skills for implementation and maintenance. This can make it difficult for small-scale farmers and rural communities to adopt and benefit from blockchain technology.
Another challenge is regulatory and legal uncertainty, as blockchain operates across multiple jurisdictions and may raise issues related to data privacy, intellectual property, and liability. Moreover, the lack of standardized protocols and interoperability can hinder the integration and scalability of blockchain in the food supply chain.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for research and collaboration to address technical, regulatory, and social issues related to blockchain in sustainable agriculture. For example, research can focus on developing user-friendly interfaces and affordable infrastructure for small-scale farmers, establishing clear legal frameworks and governance models for blockchain-based supply chain traceability, and promoting stakeholder engagement and capacity building for sustainable blockchain adoption.
Conclusion
This paper has highlighted the potential of blockchain technology in promoting sustainable agriculture by enhancing traceability, efficiency, and trust in the food supply chain. It has also discussed the challenges and opportunities of blockchain in sustainable agriculture, including technical complexity, regulatory uncertainty, and social barriers. To fully realize the benefits of blockchain in sustainable agriculture, future research and practical implementation should focus on addressing these challenges through interdisciplinary collaboration, stakeholder engagement, and capacity building. By doing so, blockchain can contribute to a more sustainable, resilient, and equitable food system.